Principles of Design Are Used in Pieces of Art
Inside: The ultimate collection of principles of pattern examples and definitions, plus helpful resources for teaching the elements and principles of fine art.

What are the Elements and Principles of Art?
The elements of art and principles of design are the central pieces that make up an artwork. Most works of art volition make apply of many or all of the elements and principles of art. We frequently gauge art by how effectively the artist used these design fundamentals even before we learn nearly them.

The elements of fine art are the edifice blocks of an artwork: color, line, shape, form, value, texture, and space. They are the tools artists use when creating an artwork. See Elements of Art Examples and Definitions for more on the elements of art.

The principles of design are how those building blocks are arranged: contrast, rhythm, proportion, balance, unity, emphasis, movement, and diversity. They are the ways an creative person can organize the elements of fine art to create a wide range of effects.
Each of these art fundamentals are closely related and many of them overlap. When combined, they produce a complete artistic vision.
Why are the Elements and Principles of Art Important?
Knowing the elements and principles of art boosts visual literacy. Artists and creators brand more than powerful works when they employ the principles of art. When viewers are familiar with the elements of art, they go more aware of the details and can better appreciate what they meet and the message behind it. Connecting with fine art makes usa more empathetic and strengthens the material of club. In the historic period of the internet, understanding how and why advertisers make design decisions tin empower students with information and brand them less susceptible to manipulation.
Teaching the Elements of Art and Principles of Design
I once said that I hate the elements and principles of art, just that'southward not quite authentic. The elements and principles of art are a lens through which to view and understand art, but they are non what makes art education vital. Art inspires college level thinking, focus, a growth mindset, visual literacy, curiosity, respect, and connection. The elements and principles of design are an creative person's toolbox. Knowing the tools not simply improves students' studio art skills and gives them deeper appreciation when viewing artworks, it helps brand them better, more than informed citizens and prepares them for a visually complex and culturally interconnected modernistic earth in need of creative problem solvers.
Below you'll find an caption of each of the principles of design, including artwork examples and links to helpful materials for teaching the individual concepts.
Please note, this mail includes Amazon affiliate links. Equally an Amazon Acquaintance I earn from qualifying purchases.
Download the Free Elements and Principles Printable Pack

This pack of printables was designed to work in a variety of means in your classroom when didactics the elements and principles of fine art. Y'all can print and hang in your classroom as posters/anchor charts or you can cutting each chemical element and principle of art in its ain individual card to use as a lesson manipulative.

Principles of Pattern Examples and Definitions
Coil beneath for each element or click the link to be taken to the advisable principle of blueprint:
- Contrast
- Rhythm
- Proportion
- Balance
- Unity
- Emphasis
- Movement
- Variety
Contrast
Equally a principle of art, contrast refers to the organisation of opposite elements and effects. For example, light and dark colors, polish and rough textures, large and small-scale shapes. Contrast tin can be used to create variety, visual interest, and drama in an artwork.
In this case of dissimilarity in art, Caravaggio created a scene of action and energy past contrasting both light/nighttime and directional lines.
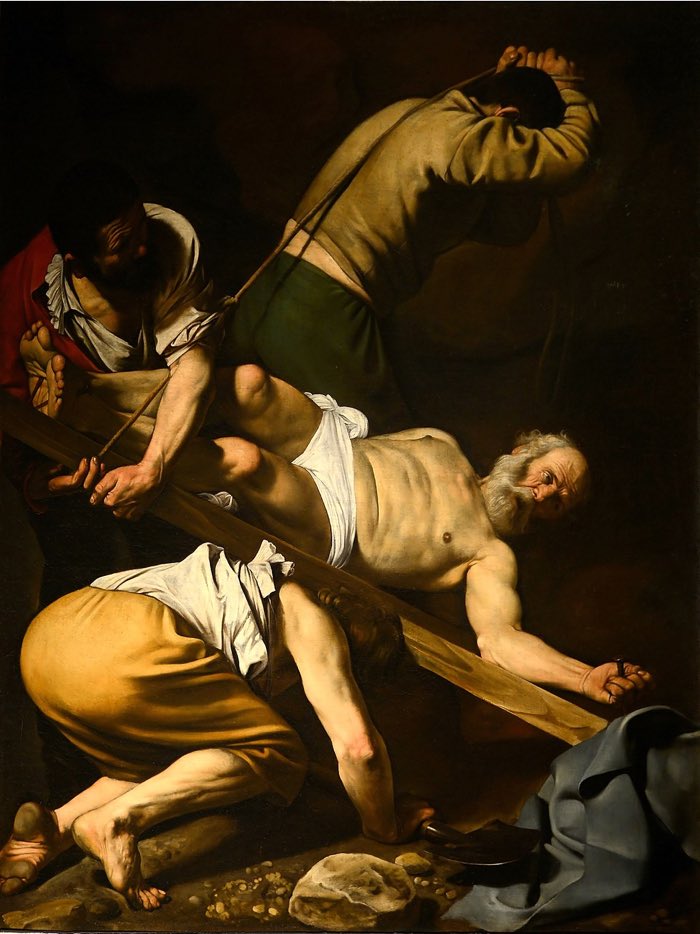

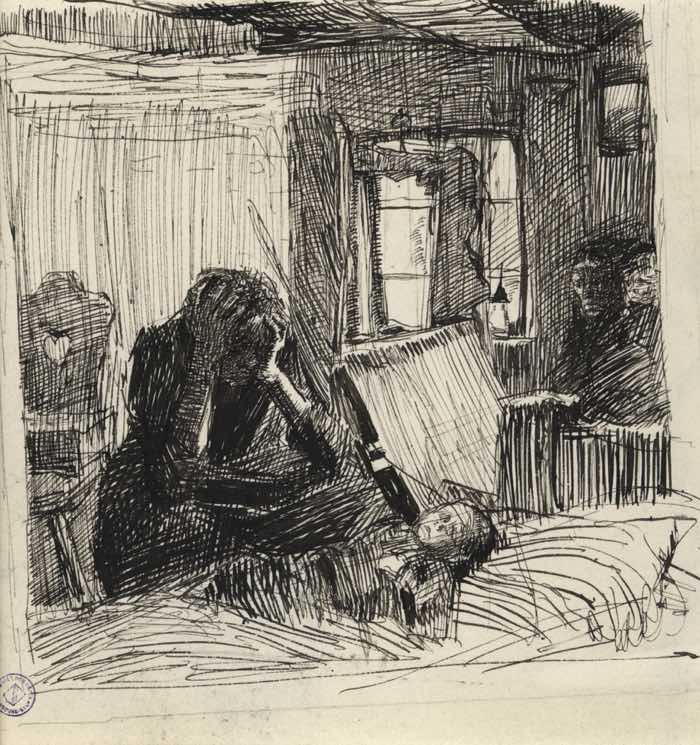
Käthe Kollwitz adds contrast using the elements of art line, value, and shape, but she besides adds contrast of emotion showing the despair of the mother in dark values and lighter sweeter elements like the center on the chair in the groundwork.

Contrast in Art Resources
- The Paper Mill Shop: Design Principles, Contrast
- Jon Lovett: Contrast, Principles of Pattern
- Edvard Munch Art Lesson with Projection
- Judith and Holofernes Paintings: A Compare and Dissimilarity Fine art Lesson
Rhythm
Rhythm is a principle of blueprint that suggests movement or activity. Rhythm is ordinarily achieved through repetition of lines, shapes, colors, and more. It creates a visual tempo in artworks and provides a path for the viewer's centre to follow.

In this rhythm example, the artist uses pattern, repetition of line, and contrast betwixt curved and straight lines to create rhythm in art.

In this example of of rhythm in fine art, Mondrian repeats shape, color, and line to bounce the viewer's middle around the artwork.
In this fun rhythm in art examples video, the differences between pattern, repetition, and rhythm are described and put to music.
Rhythm in Art Resources
- Art Soup Video: Principles of Design: Rhythm
- Equus caballus in Motion & The Start Moving Pictures
- Early on Photography Inspired Flipbook Project
Proportion
Proportion is the size relationship between the diverse parts of an artwork. Artists can use the scale and proportion to create sensations such every bit depth, realism, disorientation, and drama.

The human effigy is scaled to appear larger than the city skyline. The proportions could indicate depth of perspective or could symbolize the human relationship of laborers in edifice a urban center.
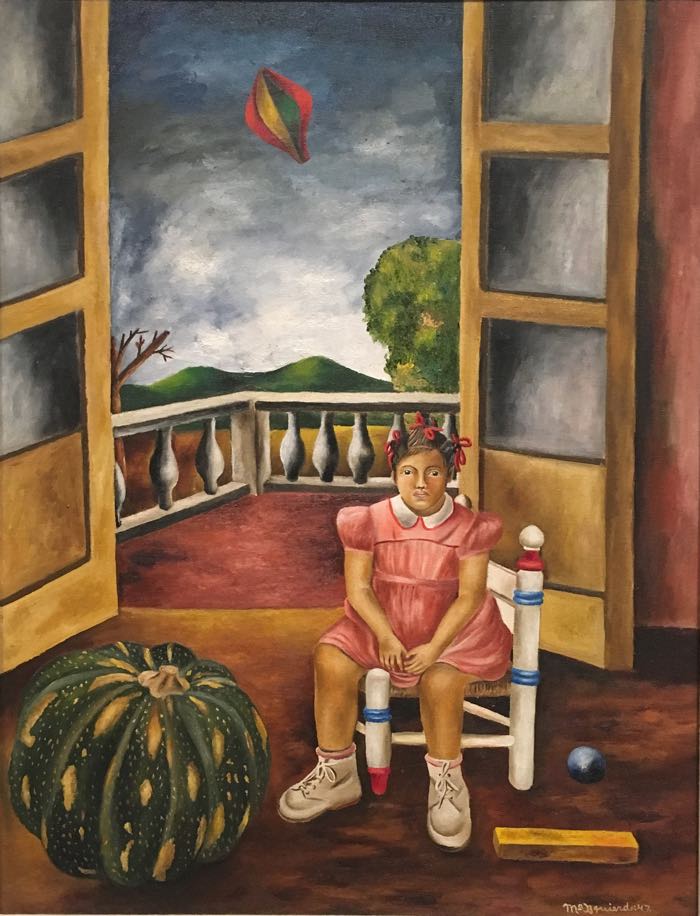
In this example of proportion in fine art, the artist manipulates the individual proportions of the child every bit well every bit create varying size relationship (scale) betwixt the objects in the painting and the child to create pregnant in the artwork.

In this proportion in art case, the artist make the easily out of proportion with the rest of their bodies to raise the significant of the artwork. These men work with their hands, and their hands are exaggerated to show how important their hands and piece of work are to all the people of France.

Looking for more than examples of proportion in art? Check out The Ultimate List of Proportion and Scale in Art Examples mail service!
Scale
Scale in art describes the size of one object in relation to another and also refers to our perception of perspective and proportion. Artworks that await realistic are scaled similarly to real world objects. Scale in fine art tin also refer to the overall size of the piece of work.
In this calibration in fine art case, the creative person uses scale to show the space or depth between the girl and the house in the background.

In this instance of scale in art, Magritte plays with calibration to create an amusing composition.
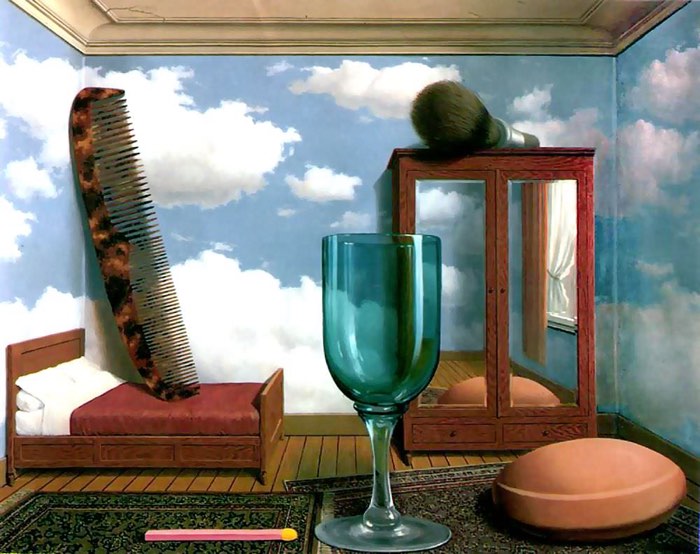

Hierarchical Calibration
Hierarchical scale is a technique used in fine art, nearly often in sculpture and painting, in which the artist depicts objects with an unnatural calibration to testify their importance or lack thereof. This size manipulation draws the viewer's eye where the artist wants attention.
Ancient Egyptian artists are well-known for their use of hierarchical scale. In this example of hierarchical calibration in art, the artist shows the man every bit largest (nigh important) and the child smallest (least important). The figures are in proportion within the figure just out of proportion with the other figures in the picture.

For more examples of scale in art, check out our proportion and scale in fine art blog mail!
Proportion in Art Resource
- The Ultimate Collection of Proportion in Art
- How Artists Depict Space
- Fine art Around the World in 30 Days – Twenty-four hour period #24 – Columbia'south Fernando Botero
- Sophia.org: Blueprint in Fine art: Scale and Proportion
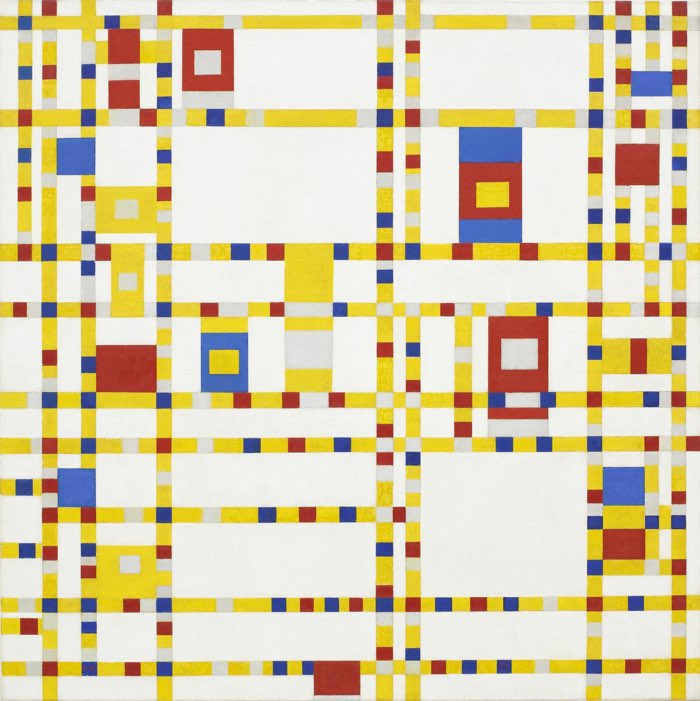
Residual
As a principle of art, balance refers to the distribution of weight in a limerick. While actual weight is a gene in sculpture and architecture, the principle of balance most often refers to the visual heaviness of shapes and forms in an artwork. An artwork's rest affects the equality and tension of the composition and can lend a feeling of calm or chaos to the work.
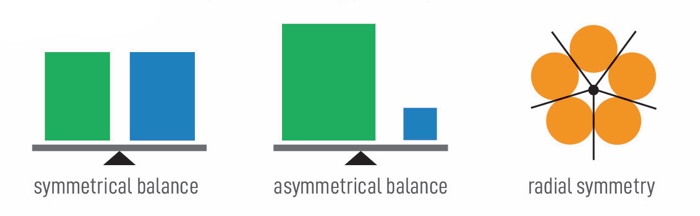
Symmetrical Residuum
An artwork with symmetrical remainder is well-counterbalanced and looks even and stable. When 1 side of an artwork mirrors the other, it has absolute symmetry. When the symmetrical balance is non exact, it is called bilateral symmetry.
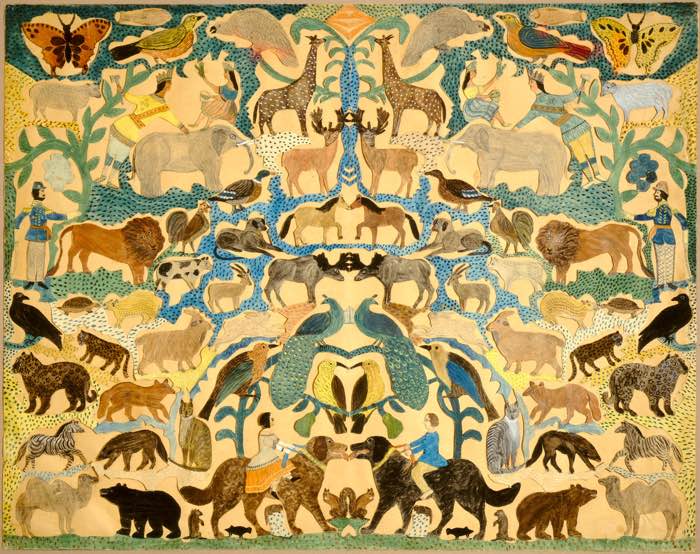
In this example of symmetrical balance in art, each animal on the left has its equal counterpart on the right. The colors are not exact, but information technology is still considered symmetrical residue.

Asymmetrical Balance
An artwork with asymmetrical balance is "heavier" or "lighter" in some areas, looks unstable, and tin can make the viewer uncomfortable. Asymmetric residuum adds a dynamic await to artworks and frequently draws attending to focal points in the composition.
In this example of asymmetrical balance in art, the creative person balances the heavy black figure on the right with the curtain on the left. If the drapery were a different size or a different color, the rest would be thrown off.

Radial Residue
An artwork with radial residual is arranged around a fundamental component. Forms and objects in a radially balanced composition announced to radiate out of the circular focal betoken of the artwork.
With radial rest, like in the example of radial balance beneath, 1 can imagine the artwork every bit equal pieces of a pie.
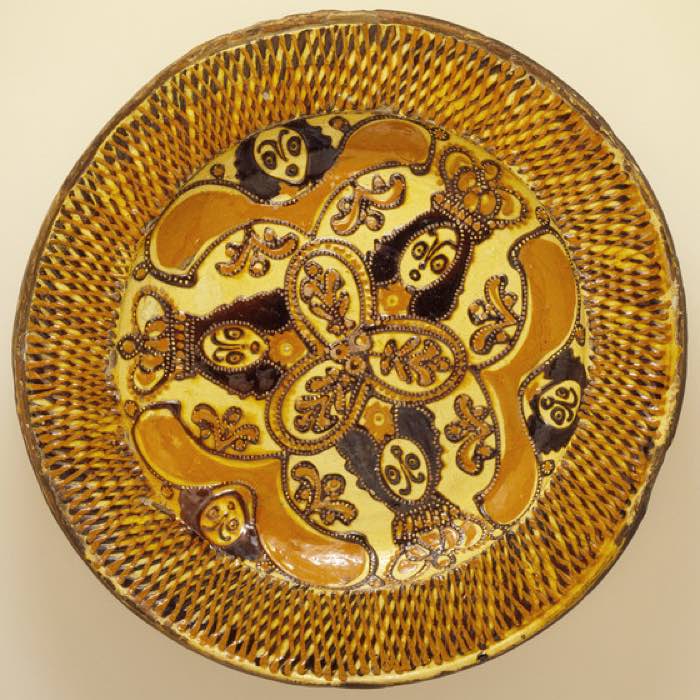

Looking for more examples of balance in art? Check out The Best Examples of Balance in Art post!
Rest in Art Resource
- The Ultimate Collection of Residual in Fine art
- Smashing Magazine: Design Principles: Compositional, Symmetrical, and Asymmetrical Residue
- Lifewire: Balance: The Basic Principles of Pattern
Unity
Unity, also known as harmony, is a design principle that refers to the cohesiveness of an artwork—how whole, consistent, and complete it appears. Unity in fine art is not necessarily simply a repetition of the same element over and over once again, just it is the pleasing combination of elements to create a harmonious composition.
In this case of unity in fine art, Botero creates unity through subject matter, through rhythm, and through repetition of grade, shape, and color.
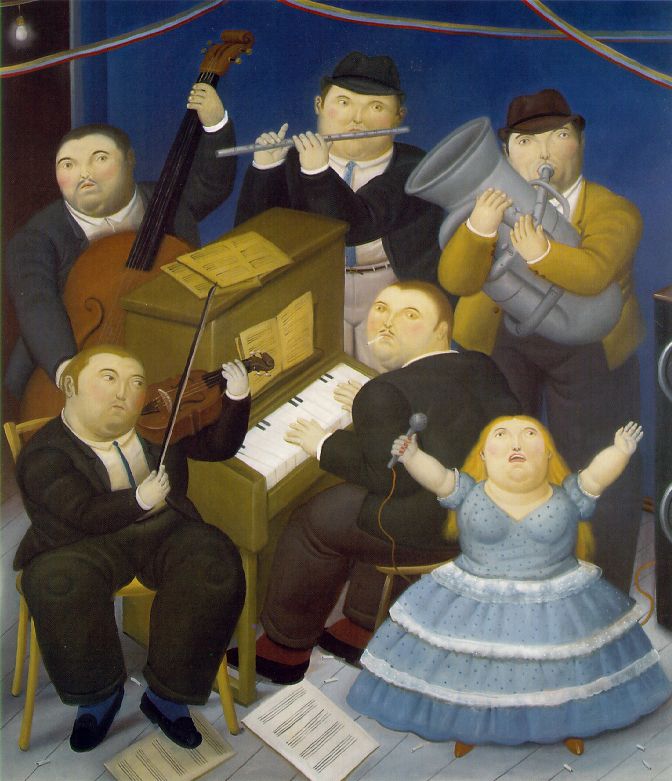

In unity blog post, you will discover more examples of unity in fine art created with shape/form, color, texture, line, manner, and in architecture.
Unity in Art Resources
- Examples of Unity in Art
- Natomas High School Design Department
- Virtual Art Instructor: Teach harmony and unity with a game
Accent
Every bit a principle of art, emphasis refers to the area of an artwork that dominates attending or draws interest. Information technology is often the place a viewer looks first. Artists create emphasis by contrasting the elements of art, such as color or shape.
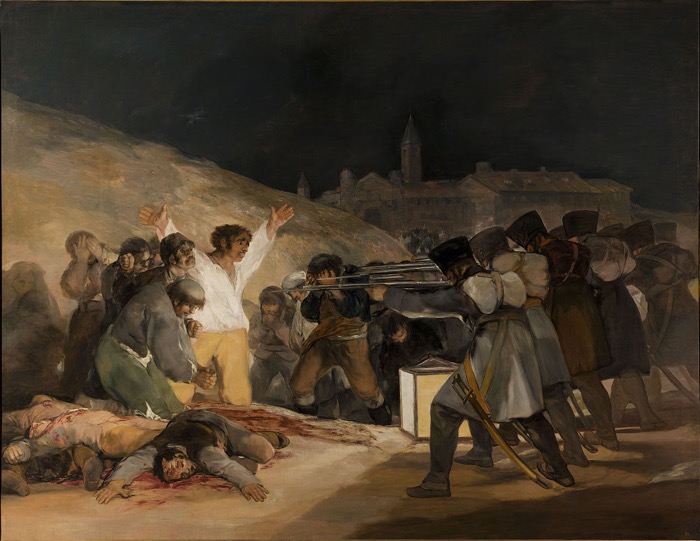
In this case of emphasis in fine art, Goya highlights the human in white through putting him in a spotlight, having the man wear bright clothes, having many lines throughout the composition pointing to the human being, and having his emotional confront be one of the just faces shown.

Looking for more examples of emphasis in fine art? Cheque out The Best Examples of Accent in Art post!
Emphasis in Fine art Resource
- The Ultimate Collection of Emphasis in Art
- Sophia.org: Design in Art: Emphasis, Variety, and Unity
Movement
Movement can be thought of in two ways – the start refers to how an creative person depicts movement using the elements and principles of art. The second way refers to the visual flow of an artwork, indicated by the path a viewer'south optics take as they look at the artwork.
Lines, edges, shapes, and colors can be utilized by the artist to point the way through an artwork equally a map for our optics to follow.
In this example of movement in fine art, the creative person shows the movement of the wind through the shapes of the paper. The lines of the figures and the lines of the billowing wearable convey movement in art equally well.
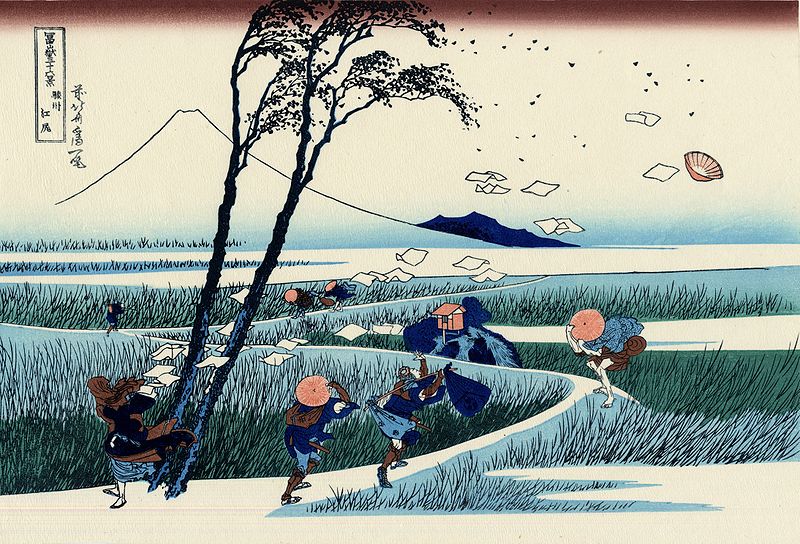

Motility in Fine art Resources
- Fine art, Design, and Visual Thinking: Movement
- Fine art About Beloved: Oskar Kokoschka'south The Bride of the Air current
- Fate of the Animals by Franz Marc
Variety
Variety refers to the elements of a composition that differ from one another. Diverseness creates visual involvement and energy.
A lot of variety can make an artwork look busy or overwhelming. When paired with unity, variety offers the viewer points of interest.
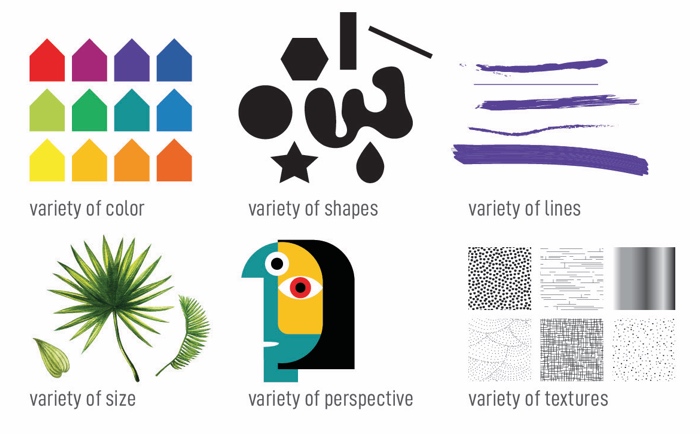
In this case of diversity in art, Kandinsky uses a multifariousness of lines, shapes, values, and colors.

Variety in Fine art Resource
- The Virtual Teacher: Variety, Harmony, and Unity
The principles of design examples tin can be a powerful mode to engage and translate a work of art. To aid your students engage, don't forget to download these free art worksheets:

Free Worksheets
8 Gratuitous Art Appreciation Worksheets
includes the Elements & Principles!
Download 8 Free Art Appreciation Worksheets – including two Elements and Principles pages! Activities designed to work with almost any work of fine art. Help your students connect with art while having fun!
More Principles of Design Examples
For more examples of elements and principles of art, check out more from our elements of art examples series below.












Source: https://artclasscurator.com/principles-of-design-examples/#:~:text=The%20principles%20of%20design%20are,a%20wide%20range%20of%20effects.
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Principles of Design Are Used in Pieces of Art"
Posting Komentar